In this post, we will look at how to use Direct Query vs Import with Power BI.
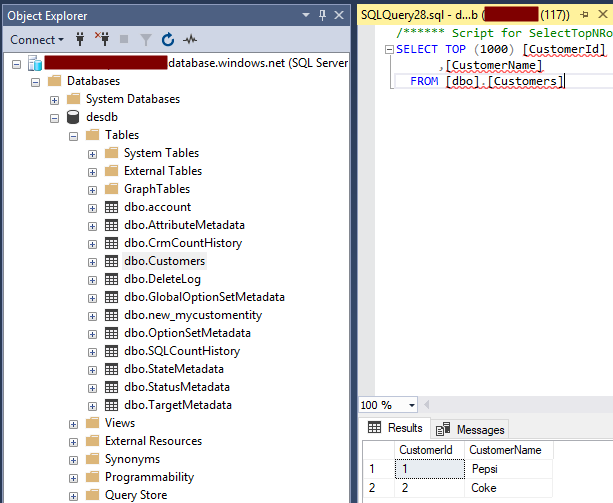
First, create a database and table, and populate it with some values. In this case, we have the Customers table with 2 records:
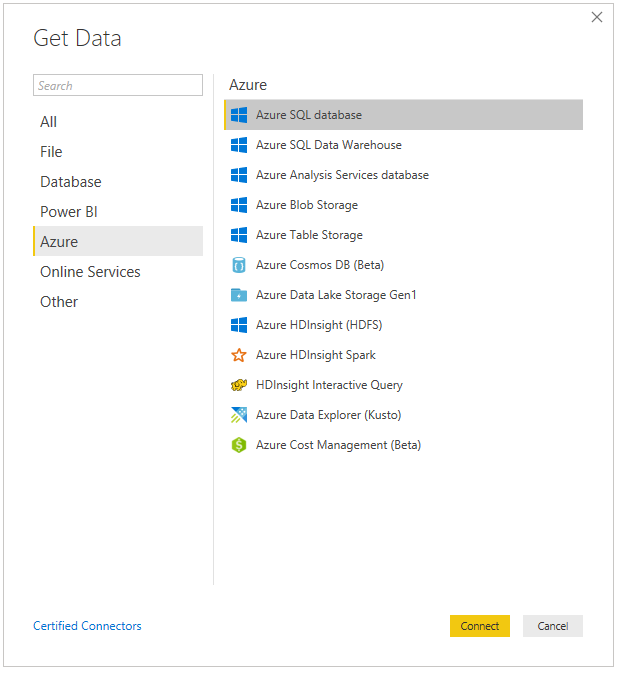
In Power BI Desktop, click on Get Data and select Azure SQL Database:
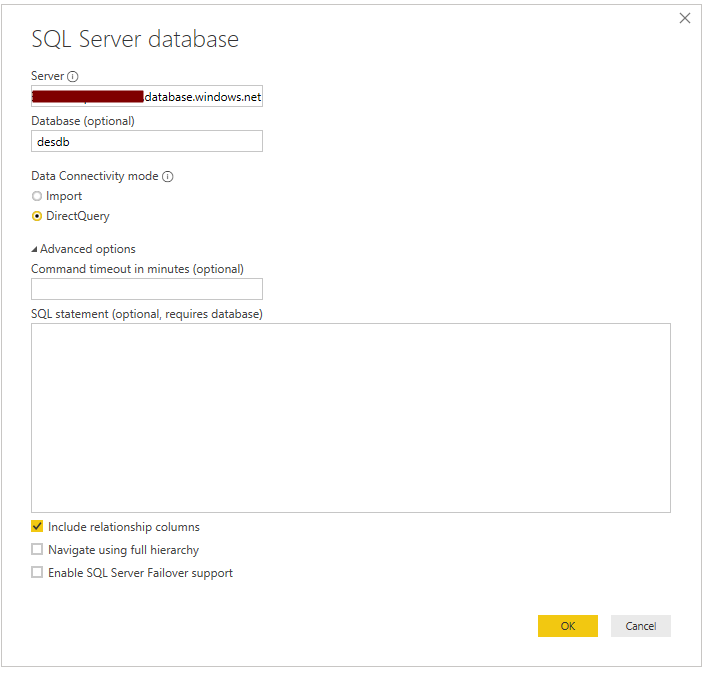
Enter the server and database name. You will see the options for Import and DirectQuery. We will select DirectQuery:
Select the Customers table and click Load:
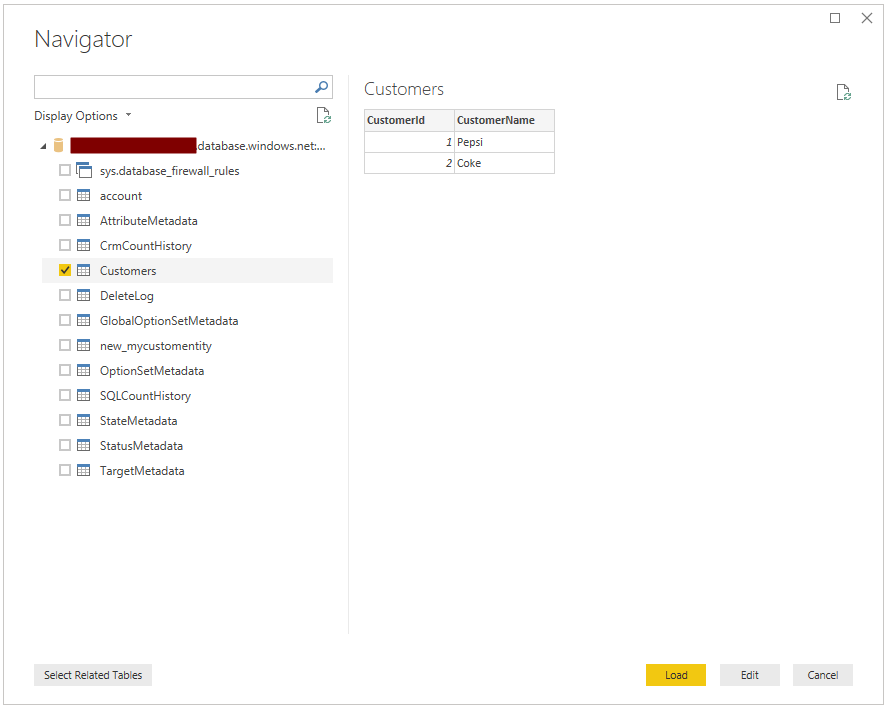
We can see the 2 rows of data:
Save and Publish. We will call the reports DQ:
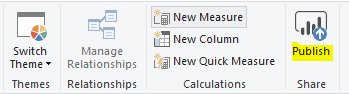
Now log into PowerBI.com. You will see “the data source is missing credentials and cannot be accessed”:
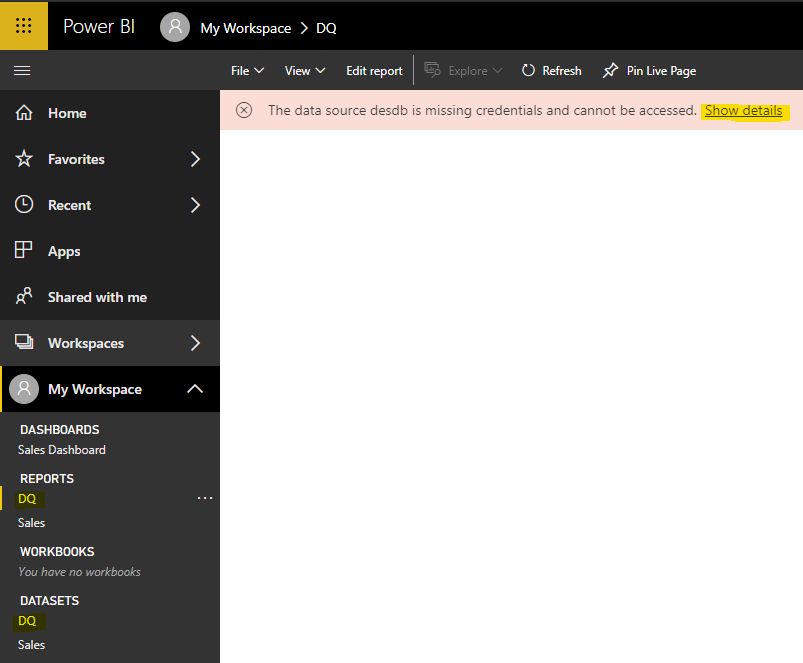
We need to set up Refresh. Click on Settings->Datasets and edit the credentials:
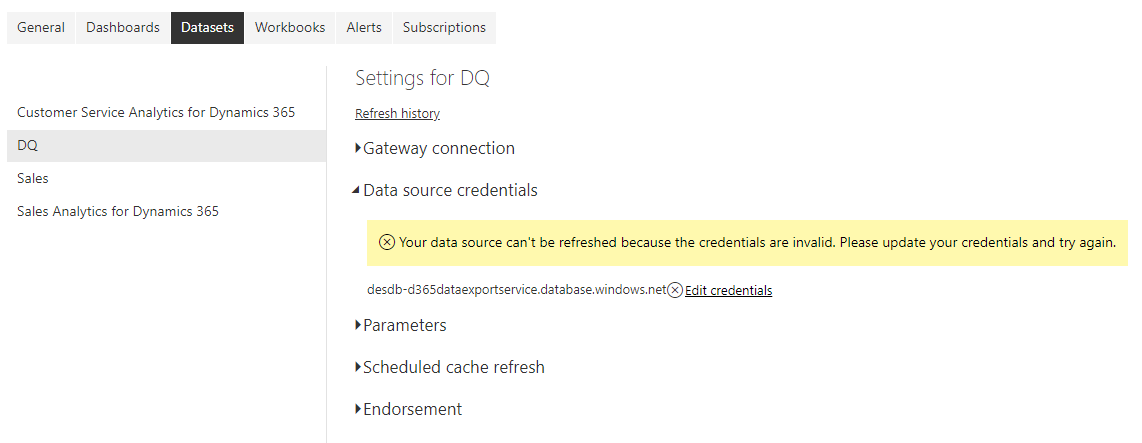
Enter SQL Server credentials here:
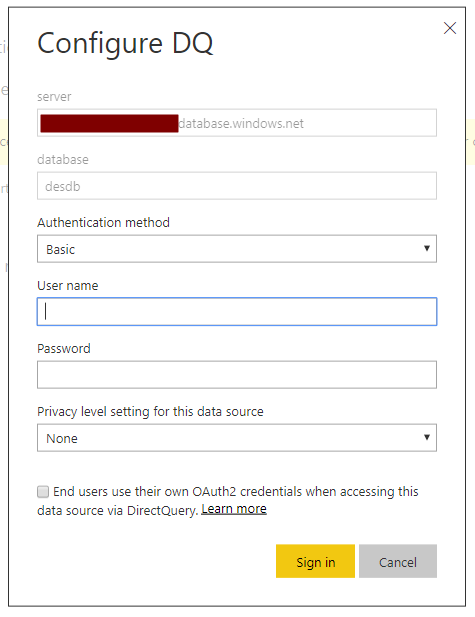
Now go back to the DQ report. You will see the data:
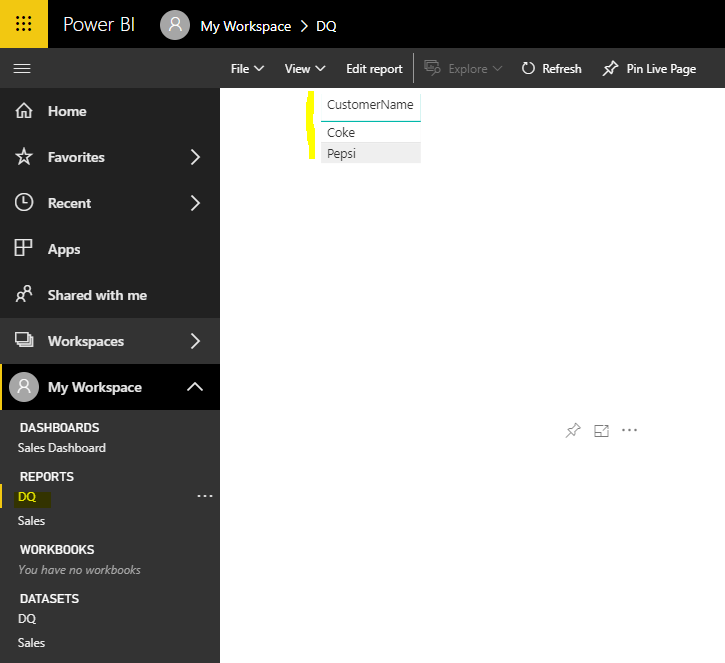
Let’s add another row directly into our SQL Server table:
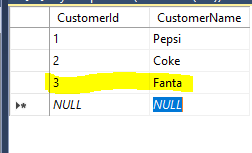
Click Refresh in the toolbar. Note we don’t need to go and refresh the whole dataset. The new record appears:
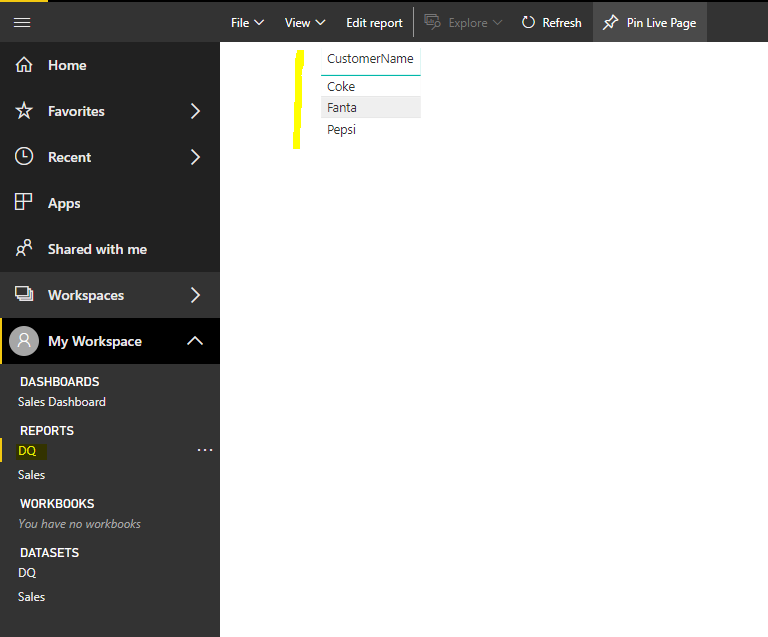
Let’s try another method. Delete the report and dataset:
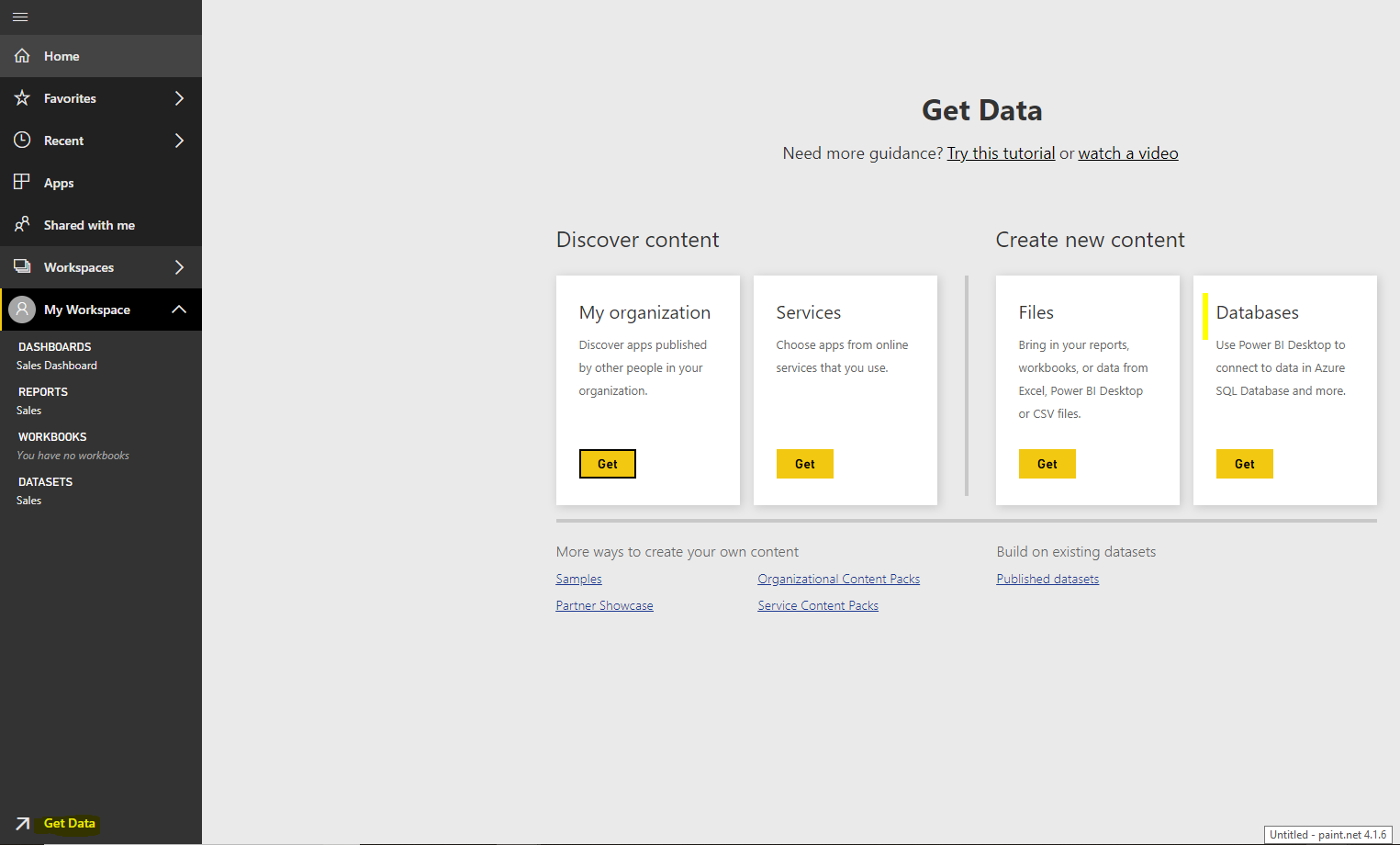
Get Data->Databases:
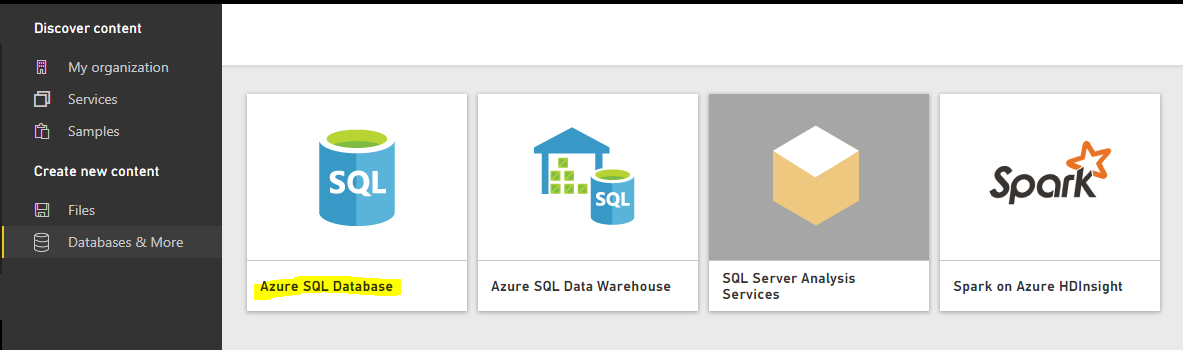
Select Azure SQL Database:
Note it says “This datasource is available in Power BI Desktop”:

Let’s compare this with Import. Create a new report and select Azure SQL database again:
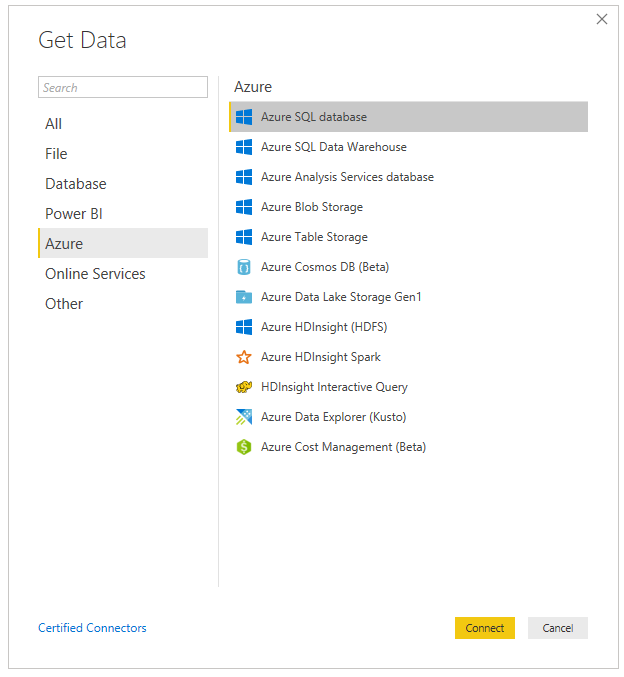
Enter the SQL Server and database, this time selecting Import:
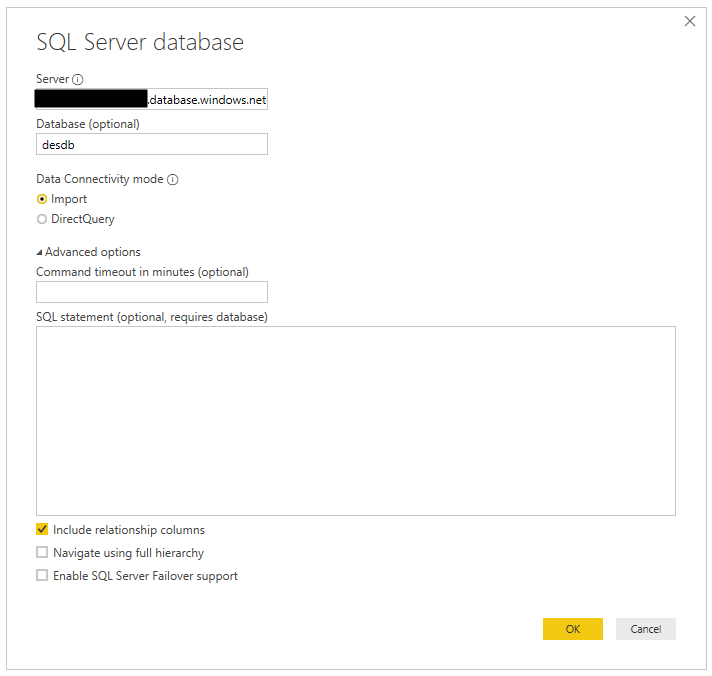
Perform the same steps to create the report, then publish. Set up the data refresh settings the same way as the Direct Query. Update the database to include a new row. Now, when you press Refresh, the data will not update:
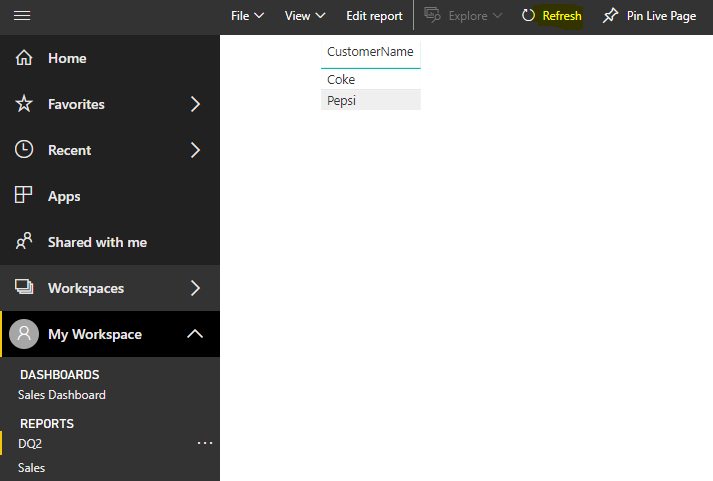
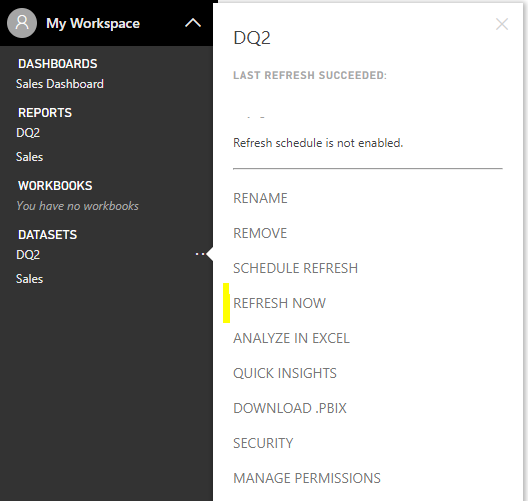
The way to get the latest data will be to do a full refresh:
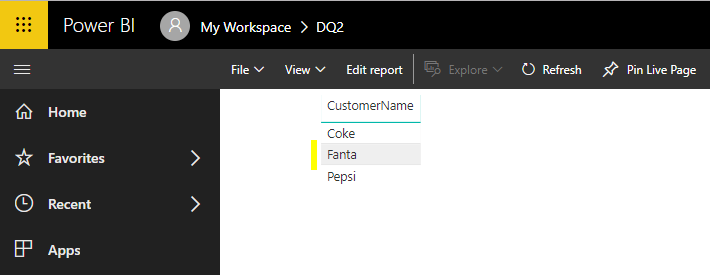
On refreshing, the data is updated. As can be seen, this is different from a Direct Query:
I AM SPENDING MORE TIME THESE DAYS CREATING YOUTUBE VIDEOS TO HELP PEOPLE LEARN THE MICROSOFT POWER PLATFORM.
IF YOU WOULD LIKE TO SEE HOW I BUILD APPS, OR FIND SOMETHING USEFUL READING MY BLOG, I WOULD REALLY APPRECIATE YOU SUBSCRIBING TO MY YOUTUBE CHANNEL.
THANK YOU, AND LET'S KEEP LEARNING TOGETHER.
CARL
