JavaScript contains different ways to handle errors.
One way is using try/catch/finally. In the example below, variable y does not exist.
try
{
var x = 1 + y;
console.log(t);
}
catch(e)
{
console.log("Error: " + e);
}
finally
{
console.log("Run finally");
}
Running this produces:
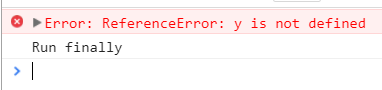
Note you can also use name, message and stack to get error information:
try
{
var x = 1 + y;
console.log(t);
}
catch(e)
{
console.error("Error: " + e.name);
console.error("Error: " + e.message);
console.error("Error: " + e.stack);
}
finally
{
console.log("Run finally");
}
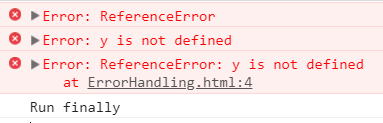
You can also throw exceptions using throw:
try
{
throw 'This is an exception';
}
catch(e)
{
console.error("Error: " + e);
}
finally
{
console.log("Run finally");
}
This produces:
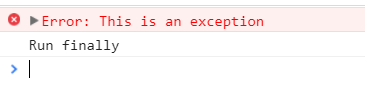
THANKS FOR READING. BEFORE YOU LEAVE, I NEED YOUR HELP.
I AM SPENDING MORE TIME THESE DAYS CREATING YOUTUBE VIDEOS TO HELP PEOPLE LEARN THE MICROSOFT POWER PLATFORM.
IF YOU WOULD LIKE TO SEE HOW I BUILD APPS, OR FIND SOMETHING USEFUL READING MY BLOG, I WOULD REALLY APPRECIATE YOU SUBSCRIBING TO MY YOUTUBE CHANNEL.
THANK YOU, AND LET'S KEEP LEARNING TOGETHER.
CARL
