Dynamics 365 and Power Apps entities come with auditing features. To enable auditing, first go to System Settings and select the Auditing tab, or go to https://admin.powerplatform.microsoft.com/ and Settings->Audit and Logs:
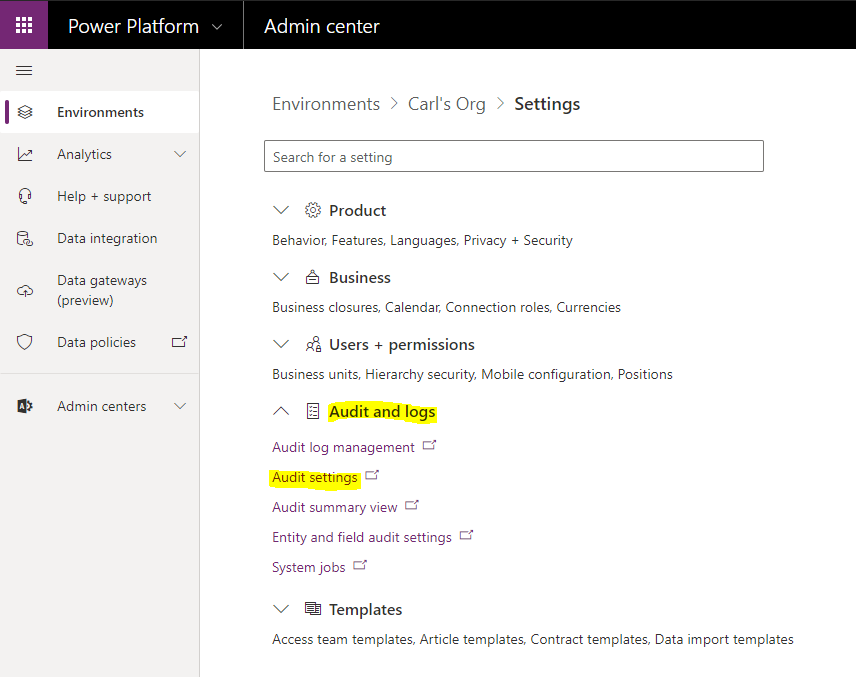
Click to Start Auditing. This enables the other checkboxes, of which the top area is:
- Audit User Access
- Start Read Auditing
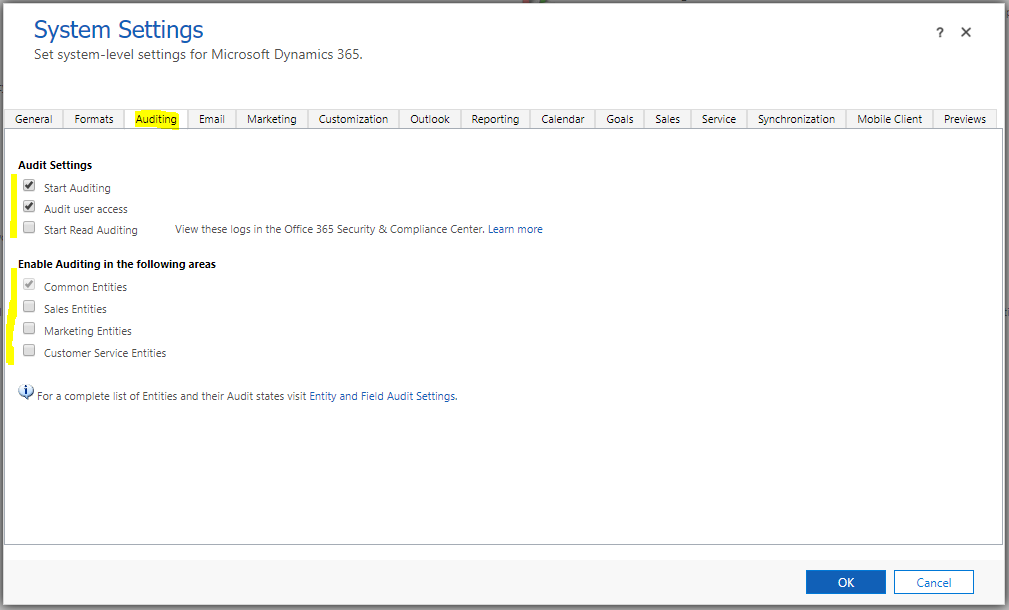
We can see the area Enable Auditing for the following areas is available to select or not. This includes:
- Common Entities. These are Account, Contact, Goal, Goal Metric, Lead, Marketing List, Product, Quick Campaign, Report, Rollup Query, Sales Literature, Security Role, User. Note when you click on Start Auditing, this Common Entities checkbox is checked by default and cannot be unchecked. When you zoom over the link, we see which of these entities already has auditing enabled and disabled. For example, we see Contact is disabled, if we were to enable it in our customizations, it would show as enabled in this list.

- Sales Entities. These are Competitor, Invoice, Lead to Opportunity Sales Process,
- Marketing Entities. This includes Campaign.
- Customer Service Entities. These include Article, Case, Contract, Expired Process, New Process, Phone to Case Process, Queue Item, Service, Social Profile, Translation Process.
Clicking on the Entity and Field Audit Settings link takes us to the Default Solution where we can select entities for auditing:
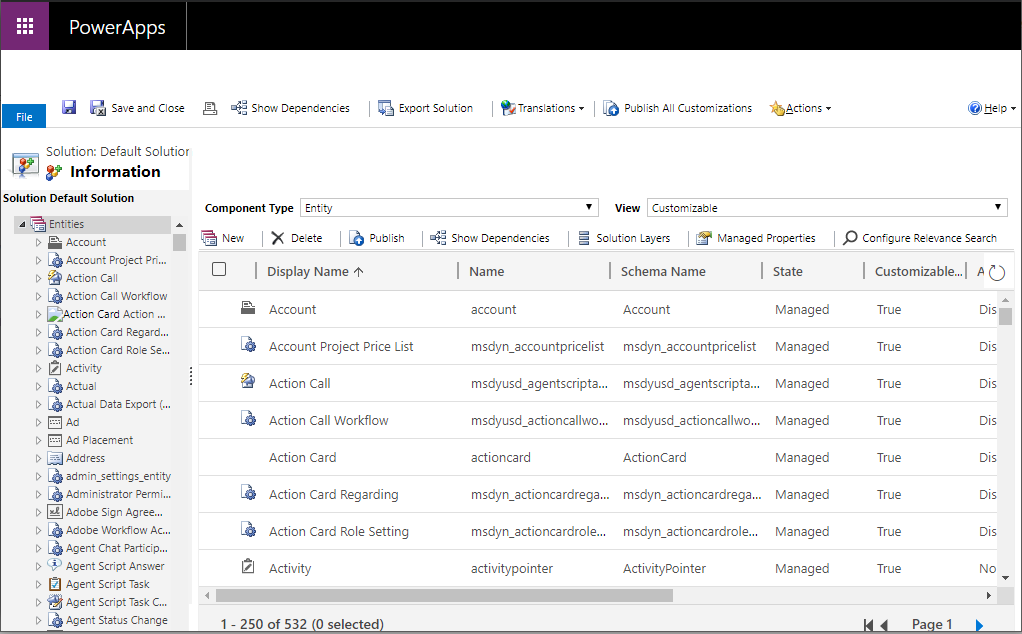
We will enable auditing for the Account entity. Open the entity in customizations and select to enable auditing. On selecting the checkbox, we get the message “By default, all fields for this entity are enabled for auditing. Choose the Fields tab to enable or disable specific fields for auditing”, with the Change Tracking checkbox selected and not editable:
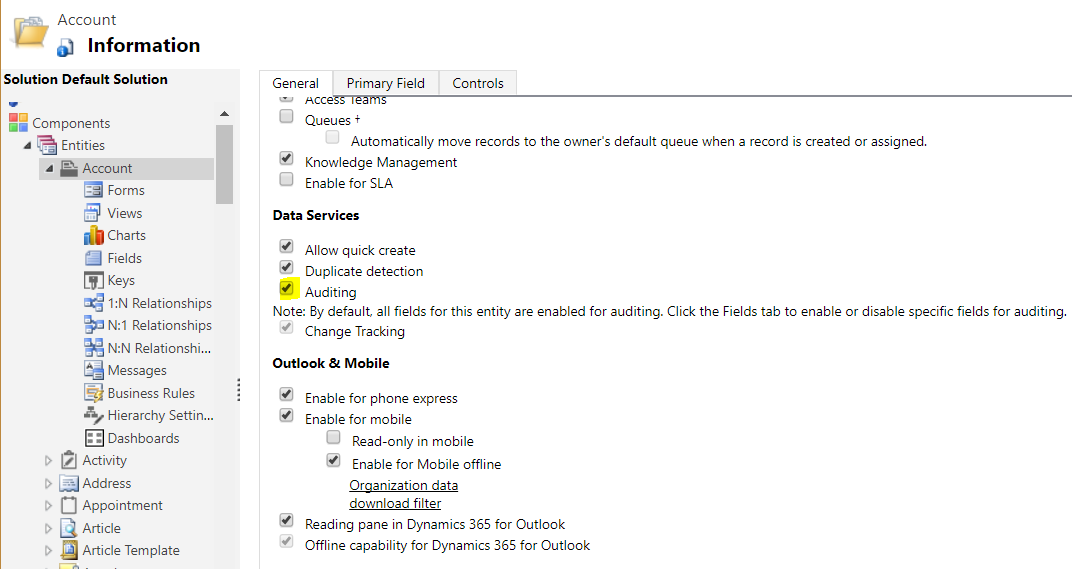
Save and publish the update.
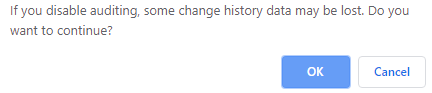
Note if you were to uncheck the Auditing checkbox now, you will get the message “If you disable auditing, some change history data may be lost. Do you want to continue?”:
Next, we will perform some actions on account records. We will update a phone number on the account entity.
On the Account record, go to Related->Audit History:
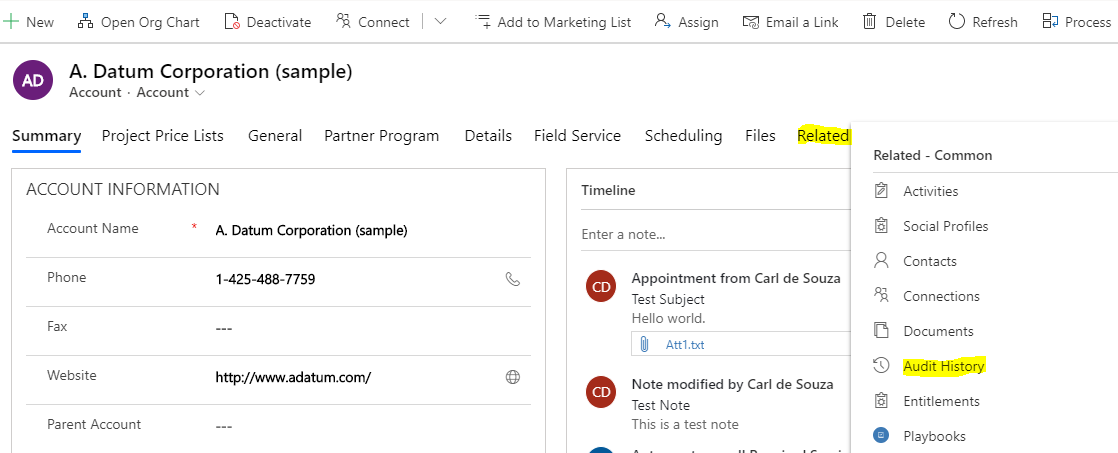
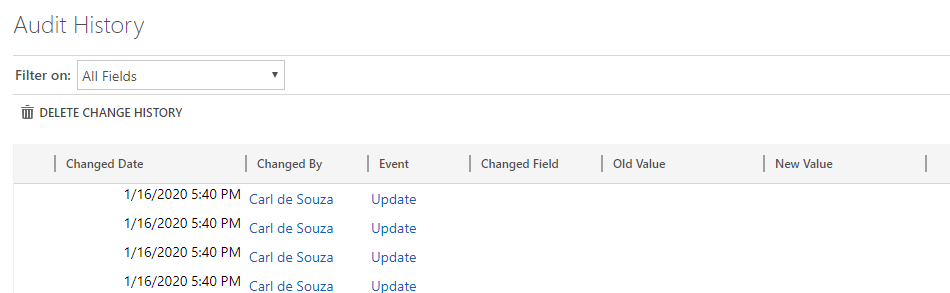
We see the Update event has occurred, but the Changed Field, Old and New Value are not populated:
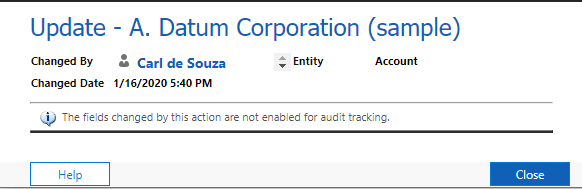
On selecting the Update link, we see “The fields changed by this action are not enabled for audit tracking”:
Ensure the field you are updating has Auditing enabled. To do this, open the field in the solution and ensure Auditing is set to Enable:
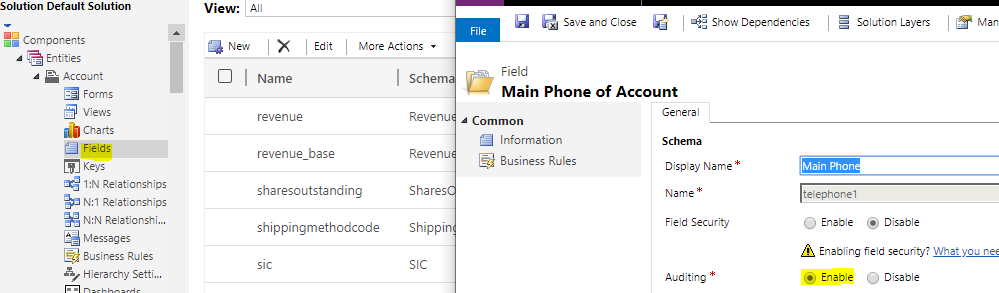
After doing so, the field now appears in the Auditing change history:
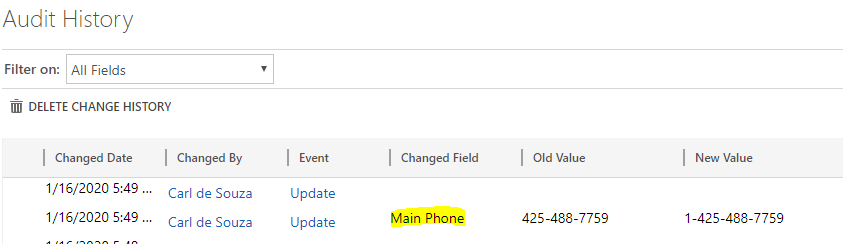
Note if we disable auditing, we see the message in the Audit History that “Audit Attribute Stopped”:
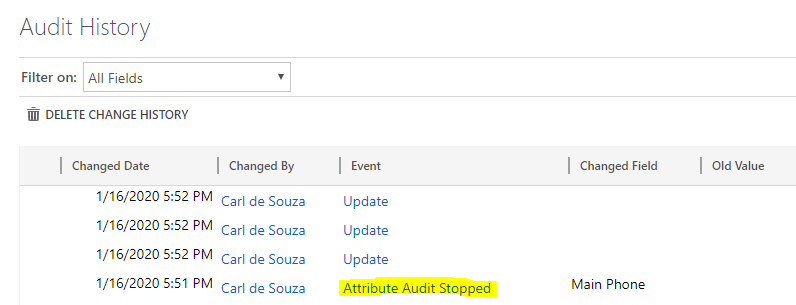
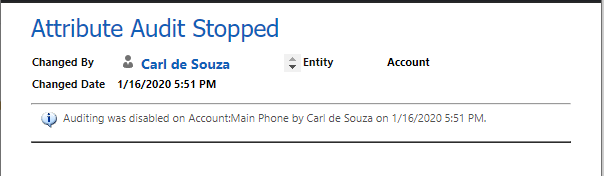
With “Auditing was disabled on Account:Main Phone”:
To view the audit logs, go to Settings->Auditing:
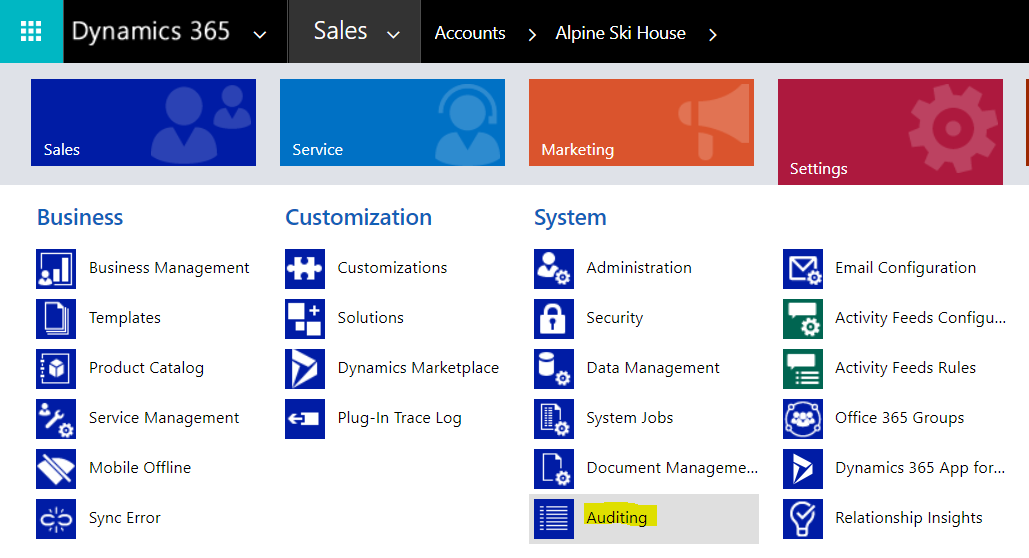
The page will open. Select Audit View Summary:

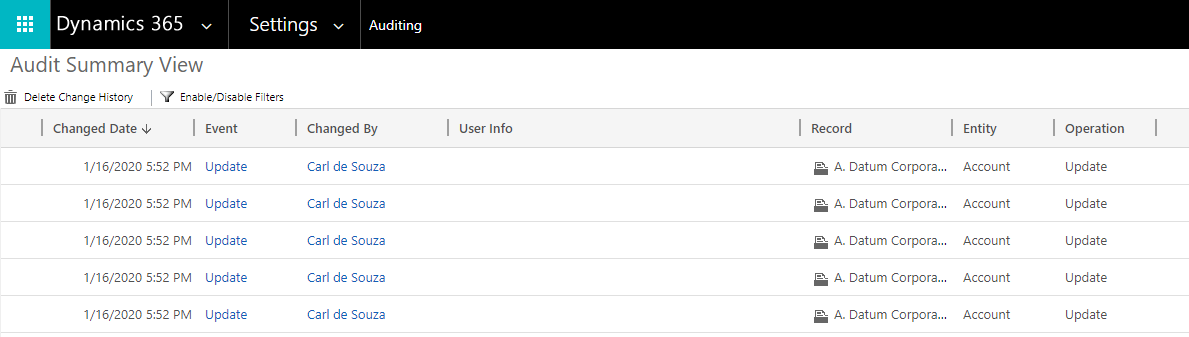
You will see the record of the update we just made:
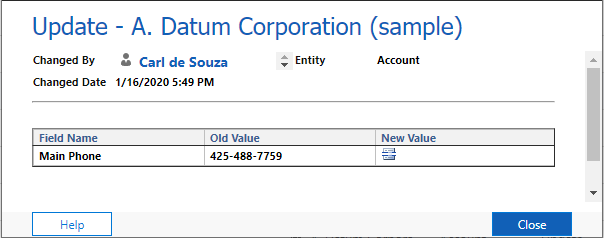
Clicking on the update will show more information:
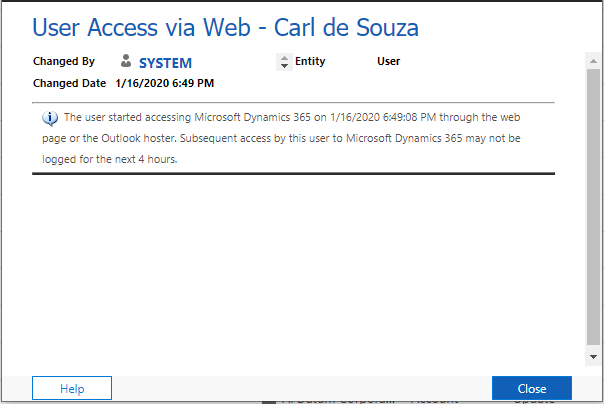
Audit User Access gives us a record for the user accessing the system:
If we enable Start Read Auditing, we need to enable under Auditing in the Account (Entity) Customizations:
- Single record auditing. Log a record when opened.
- Multiple record auditing. Log all records displayed on an opened page.

I AM SPENDING MORE TIME THESE DAYS CREATING YOUTUBE VIDEOS TO HELP PEOPLE LEARN THE MICROSOFT POWER PLATFORM.
IF YOU WOULD LIKE TO SEE HOW I BUILD APPS, OR FIND SOMETHING USEFUL READING MY BLOG, I WOULD REALLY APPRECIATE YOU SUBSCRIBING TO MY YOUTUBE CHANNEL.
THANK YOU, AND LET'S KEEP LEARNING TOGETHER.
CARL



