Abstract classes are a type of class in C# that contains a base class implementation. The abstract class is not instantiated, and are inherited by subclasses to provide a detailed implementation.
Consider the example below. We have an abtract class called Vehicle in our console app. We try to create an instance of the abtract class Vehicle:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace Carl.AbstractClass
{
class Program
{
abstract class Vehicle
{
public int wheels { get; set; }
public abstract int GetWheels();
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
try
{
Vehicle car = null;
car.wheels = 4;
Console.WriteLine("Vehicle has {0} wheels", car.wheels);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine(ex.ToString());
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
Though the code will compile, we will get an error when running the code:

In order to use the abtract class, we can create a derived class, such as Car in this example. Note when you derive from the abstract class, Visual Studio provides help on what to implement:

We will add code to our Car class, with an overrride on the GetWheels method.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace Carl.AbstractClass
{
class Program
{
abstract class Vehicle
{
public int wheels { get; set; }
public abstract int GetWheels();
}
class Car : Vehicle
{
public override int GetWheels()
{
return wheels;
}
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
try
{
Car ferrari = new Car();
ferrari.wheels = 4;
Console.WriteLine("Vehicle has {0} wheels", ferrari.GetWheels());
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine(ex.ToString());
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
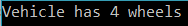
When run, this produces:
Note abstract classes can contain implementation. For example, we could have a method HowManyWheels in our abstract class, which returns a string:
abstract class Vehicle
{
public int wheels { get; set; }
public abstract int GetWheels();
public string HowManyWheels()
{
return string.Format("There are {0} wheels", wheels);
}
}
This is different from interfaces in C#, in which this implementation cannot be provided.
I AM SPENDING MORE TIME THESE DAYS CREATING YOUTUBE VIDEOS TO HELP PEOPLE LEARN THE MICROSOFT POWER PLATFORM.
IF YOU WOULD LIKE TO SEE HOW I BUILD APPS, OR FIND SOMETHING USEFUL READING MY BLOG, I WOULD REALLY APPRECIATE YOU SUBSCRIBING TO MY YOUTUBE CHANNEL.
THANK YOU, AND LET'S KEEP LEARNING TOGETHER.
CARL



